Challenges, opportunities, and solutions for the NIS2 Directive

In January 2023, EU Member States formally issued a revision to the 2016 Network and Information Systems (NIS) security Directive.
Conceived in response to several widely publicized and damaging cyber-attacks, the NIS2 Directive strengthens security requirements, streamlines reporting requirements, and introduces stricter oversight measures and enforcement requirements.
For business owners, CEOs and IT technicians, understanding NIS2 is critical to protecting their companies from cyber risks and the penalties imposed for noncompliance.
What is the NIS2 Directive?
The NIS2 Directive, or Network and Information Security Directive, is an European Union legislative update that expands and strengthens the 2016 NIS Directive.
It includes vital new areas, establishes more stringent requirements, and promotes closer cooperation among Member States.
 This is a legislative update developed and adopted by the EU Institutions, specifically the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the Council of the European Union.
This is a legislative update developed and adopted by the EU Institutions, specifically the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the Council of the European Union.
The goal of the Directive is to strengthen cybersecurity within the EU, especially in critical areas, responding to new challenges posed by the evolving digital landscape and threats.
Since this is a directive and not a regulation (as is, for example, the GDPR) it needs to be implemented by all Member States within a certain set period, in this case by October 18, 2024, developing national security plans and specialized teams to implement the Directive.
The NIS2 Directive complements the various European data protection and privacy regulations and guidelines, first and foremost the EU General Data Protection Regulation 2016/679 (GDPR) but, also the DORA Regulation, the ERC Directive, the Cyber Resilience Act and, at the national level, the National Cyber Security Perimeter.
NIS2 also introduces new categories of essential service operators (OSEs) and digital service providers (DSPs).
The object of the Directive
The object of the Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2) is to establish a common legal framework within the European Union to ensure a high level of network and information system security.
Below are presented key aspects of the NIS2 Directive scope:
Expansion of scope
Extends the scope of cybersecurity standards to new vital sectors and public and private entities, including providers of digital services such as search engines and cloud computing services.
Security requirements
Requires Member States to ensure that organizations within the specified areas take appropriate safety measures and notify relevant agencies of serious accidents.
Cooperation among Member States
Promotes closer cooperation among Member States through the NIS Cooperation Group and the Incident Response Network, facilitating information sharing and a coordinated response to large-scale incidents.
Penalties and sanctions
Establishes that Member States must have effective, proportionate and dissuasive penalty regimes for non-compliance.
Response Plans
Requires the creation of incident response plans and regular analysis of vulnerabilities and threats.
Impact on businesses
The NIS2 Directive directly impacts companies, requiring compliance and providing potential opportunities in reputation and competitiveness.
Strengthening overall resilience
The Directive’s goal is to strengthen resilience and response capabilities to cybersecurity incidents within the EU by improving preparedness, security culture, and cooperation among Member States.
Who NIS2 is aimed at
The NIS2 Directive applies to:
- Operators of essential services (OSEs)
- Providers of important digital services
- Government service providers
Let’s look at them in detail.
The category of important digital service providers in the NIS2 Directive includes a set of entities that offer essential digital services within the single market.

These may vary according to specific national implementations, but generally include:
- Search engines;
- Cloud computing services;
- Online marketplaces;
- Social networks;
- Other strategic digital services that could be considered vital to the economy and society, depending on national decisions and the evolving digital landscape.
Government service providers mentioned in the NIS2 Directive refer to government entities and public organizations that provide essential services within EU Member States.
These services can cover a wide range of sectors, and entities may include:
- Ministries and government departments;
- Government agencies;
- Local governments;
- Emergency services;
- Institutions of public education;
- Hospitals and public health services;
- Providers of critical infrastructure, such as energy, water, and transportation, if they are owned or operated by the government.
The NIS2 Directive requires these government service providers to take appropriate measures to ensure network and information security, given their critical importance to public function and societal security.
The goal is to improve the EU’s overall resilience against cybersecurity incidents and threats, recognizing that government entities play a key role in maintaining the stability and well-being of society.
The obligations imposed by the Directive
The NIS2 Directive imposes specific actions to be implemented by those it addresses to raise their level of cyber resilience.
The following is a summary list:
- Structure risk analysis and information systems security policies;
- Create cyber incident management plans;
- Ensure business continuity through actions such as backup management and disaster recovery, along with crisis response;
- Ensure supply chain security, including security aspects concerning the relationship between each entity and its direct suppliers;
- Secure the acquisition of computer and network systems development and maintenance, including vulnerability management and disclosure;
- Create strategies and procedures to evaluate the effectiveness of measures to counter cyber security risks;
- Create and adhere to basic cyber hygiene practices and ensure cybersecurity training;
- Establish policies and procedures related to the use of encryption and cryptography;
- Ensure cybersecurity for staff by setting up access control and asset management strategies;
- Use multi-factor or continuous authentication solutions, secure voice, video and text communications, and secure emergency communication systems.
As an additional step, it is made mandatory for those affected by the NIS2 Directive to promptly report IT incidents and related critical issues on the portal of the CSIRT (Computer Security Incident Response Team).
Sanctions and penalties
With the entry of the NIS2 Directive, there are different penalties, depending on whether an operator qualifies as essential or important.
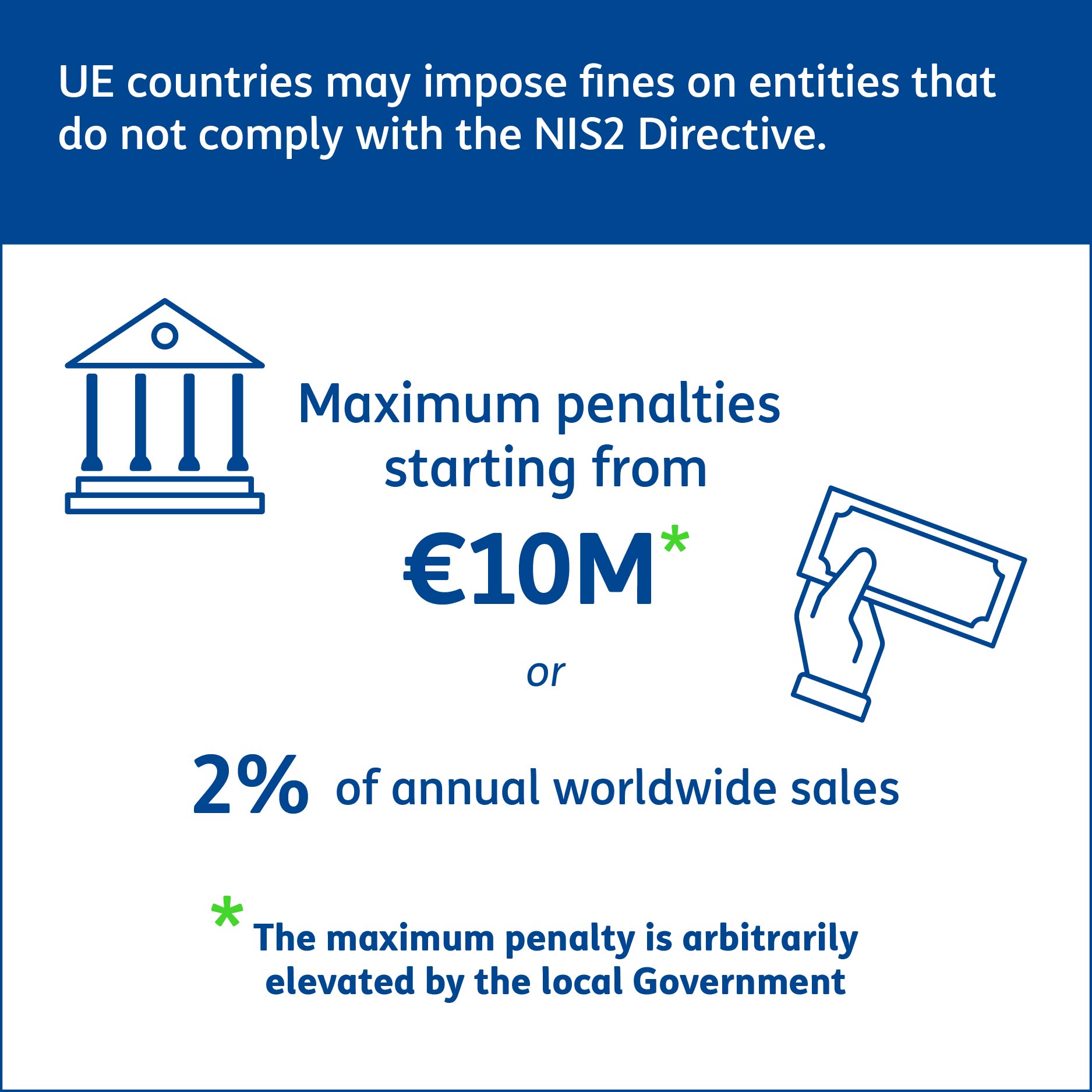 In synthesis, the types of sanctions are divided as follows:
In synthesis, the types of sanctions are divided as follows:
Essential entities
Will be subject to administrative fines of a maximum cap of at least 10,000,000 euros or a maximum of 2% of the total annual worldwide turnover for the previous fiscal year, whichever is higher and unless otherwise provided by the legislature.
Significant entities
Will be subject to administrative fines of a maximum cap of at least 7,000,000 euros or a maximum of at least 1.4% of the total annual worldwide turnover for the previous fiscal year, whichever is higher and unless otherwise provided by the legislature.
How to prepare for NIS2
Therefore, to avoid incurring IT incidents, regulatory problems or steep penalties, it is essential to rely on experts and certified, secure technologies.
For more than fifty years, Telsy’s solutions have been employed by companies and institutions for the prevention, protection, response and monitoring, including legal and procedural, of their IT systems and infrastructures.
Telsy offers its Clients proprietary technologies, developed in-house, and certified and highly skilled experts to ensure the highest quality in the delivery of data and communications security solutions.
Together with our legal experts and cybersecurity professionals, you will find everything you need to effectively respond to the regulatory adaptations imposed by the NIS2 Directive, dodging the risk of penalties and cyber incidents.
Learn more about our NIS2 dedicated solutions and contact us for more information.
